MERRA-2
MERRA-2 is a reanalysis data product from NASA/GMAO. It is currently being produced with the GMAO/GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System Version 5.12.4. MERRA-2 is intended to replace the MERRA reanalysis product (which was created with GEOS-5.2.0). It has a native resolution of 0.5° lat x 0.625° lon x 72 hybrid sigma/pressure levels. MERRA-2 data is stored on the same vertical grid as the GEOS-5 "forward processing" (what we call GEOS-FP) and MERRA met field product.
For more information, please see:
- MERRA-2 (v1.0) file specification document (25 Sept 2015)
- List of MERRA-2 met fields for GEOS-Chem
- Information about implementing MERRA-2 into GEOS-Chem
- Overview of GMAO met data products
- Glossary of variables produced by the GEOS-DAS
- Version history of GMAO met data products
Overview
NOTE: MERRA is currently being produced with the GMAO/GEOS-5 Data Assimilation system, version 5.12.4. This is a slightly newer version of the GEOS/DAS than what is used to produce the GEOS-5 "forward processing" data. The description below mostly applies to MERRA-2 data, except that the native resolution of the archived MERRA-2 data files is now 0.5° x 0.625°.
From the GEOS5-FP file specification document, Version 1.0 (11 Jun 2013), p. 1:
The GEOS-5 FP Atmospheric Data Assimilation System (GEOS-5 ADAS) uses an analysis developed jointly with NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), which allows the Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) to take advantage of the developments at NCEP and the Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation (JCSDA). The GEOS-5 AGCM uses the finite-volume dynamics (Lin, 2004) integrated with various physics packages (e.g, Bacmeister et al., 2006), under the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF) including the Catchment Land Surface Model (CLSM) (e.g., Koster et al., 2000). The GSI analysis is a three-dimensional variational (3DVar) analysis applied in grid-point space to facilitate the implementation of anisotropic, inhomogeneous covariances (e.g., Wu et al., 2002; Derber et al., 2003). The GSI implementation for GEOS-5 FP incorporates a set of recursive filters that produce approximately Gaussian smoothing kernels and isotropic correlation functions.
The GEOS-5 ADAS is documented in Rienecker et al. (2008). More recent updates to the model are presented in Molod et al. (2011). The GEOS-5 system actively assimilates roughly 2 × 106 observations for each analysis, including about 7.5 × 105 AIRS radiance data. The input stream is roughly twice this volume, but because of the large volume, the data are thinned commensurate with the analysis grid to reduce the computational burden. Data are also rejected from the analysis through quality control procedures designed to detect, for example, the presence of cloud.
To minimize the spurious periodic perturbations of the analysis, GEOS-FP uses the Incremental Analysis Update (IAU) technique developed by Bloom et al. (1996).
The assimilation is performed at a horizontal resolution of 0.3125-degree longitude by 0.25-degree latitude and at 72 levels, extending to 0.01 hPa. All products are generated at the native resolution of the horizontal grid. The majority of data products are time-averaged, but four instantaneous products are also available. Hourly data intervals are used for two-dimensional products, while 3-hourly intervals are used for three-dimensional products. These may be on the model’s native 72-layer vertical grid or at 42 pressure surfaces extending to 0.1 hPa.
--Bob Y. 15:00, 16 August 2013 (EDT)
Version history
The following table lists the GMAO data version numbers corresponding to specific dates in our GEOS-FP met field archive for GEOS-Chem:
| GMAO version number |
Dates produced | Start date (in our MERRA-2 archive) |
End date (in our MERRA-2 archive) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEOS-5.12.4 "MERRA-2_100 Stream" |
1979-1990 | TBD | TBD |
| GEOS-5.12.4 "MERRA-2_200 Stream" |
1991-1999 | TBD | TBD |
| GEOS-5.12.4 "MERRA-2_300 Stream" |
2000-2009 | TBD | TBD |
| GEOS-5.12.4 "MERRA-2_400 Stream" |
2010- | TBD | TBD |
--Bob Y. (talk) 18:11, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
Acknowledge the source of MERRA-2 data in your publications
If your GEOS-Chem research depends on the MERRA-2 meteorological data producs, please consider adding an acknowledgment to your citations, such as:
The MERRA-2 data used in this study/project have been provided by the Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
--Bob Y. (talk) 19:25, 3 August 2015 (UTC)
Developers
The following table credits the various individuals who have assisted with the development of the MERRA-2 met data product and its incorporation into GEOS-Chem:
| Developers | Feature |
|---|---|
| NASA/GMAO | Creation of GEOS-FP assimilated meteorological data product |
| Bob Yantosca (GCST) | Creation of MERRA-2 data processing software |
| GEOS-Chem Support Team | Making GEOS-Chem compatible with MERRA-2 met data |
--Bob Y. (talk) 19:21, 3 August 2015 (UTC)
MERRA-2 grid structure
This section describes the horizontal and vertical grids used by the GEOS-FP data products.
Input grids
From the GEOS5-FP file specification document, Version 1.0 (11 Jun 2013), p. 7:
Fields are produced on the model’s native horizontal grid, with a resolution of 5/16 degree longitude by 1/4 degree latitude.
The GEOS5-FP global horizontal grid consists of IMn=1152 points in the longitudinal direction and JMn=721 points in the latitudinal direction. The horizontal native grid origin, associated with variables indexed (i=1, j=1) represents a grid point located at (180°W, 90°S). Latitude and longitude of grid points as a function of their indices (i, j) can be determined by:
Lon(I) = -180° + [ ΔLon * ( I - 1 ) ], I = 1, IMN
Lat(I) = -90° + [ ΔLat * ( J - 1 ) ], J = 1, JMN
Where ΔLon = 5/16° = 0.3125° and ΔLat = 1/4° = 0.25°. For example, (i = 577, j = 361) corresponds to a grid point at ( 0, 0).
and also on p. 7:
Gridded products use four different vertical configurations: horizontal-only (can be vertical averages, single level, or surface values), pressure-level, model-level, or model-edge. Horizontal-only data for a given variable appear as 3-dimensional fields (x, y, time), while pressure-level, model-level, or model-edge data appear as 4-dimensional fields (x, y, z, time). In all cases the time dimension spans multiple files, as each file (granule) contains only one time. Pressure-level data is output on the LMp=42 pressure levels shown in Appendix B. The model layers used for GEOS-5 FP products are on a terrain-following hybrid sigma-p coordinate. Model-level data is output on the LM=72 layers shown in the second table of Appendix B. The model-edge products contain fields with LMe = LM + 1 levels representing the layer edges. The pressure at the model top is a fixed constant, PTOP=0.01 hPa. Pressures at model edges should be computed by summing the DELP(I,J,L) starting at PTOP. A representative pressure for the layer can then be obtained from these. In the GEOS-4 eta files, one could compute the pressure on the edges by using the “ak” and “bk” values and the surface pressure. In GEOS-5, the full 3-dimensional pressure variables are explicitly provided through (DELP(I,J,L)) and PTOP. Even though the model-level fields are on a hybrid sigma-p coordinate and their vertical location could be obtained from the “ak-bk” relationship, this may change in future GMAO systems. We thus recommend that users rely on the reported 3D pressure distribution, and not use ones computed from the “ak” and “bk”.
Note that the indexing for the GEOS-5 FP vertical coordinate system is top to bottom, i.e., layer 1 is the top layer of the atmosphere, while layer LM is adjacent to the earth’s surface. The same is true for edge variables, with level 1 being the top of the model’s atmosphere (PTOP), and level LM+1 being the surface.
The table below lists the combination of the horizontal and vertical grids onto which the GEOS-FP "raw" data products are placed:
| Grid | Name | Horizontal Resolution |
Vertical Resolution |
Used for | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal-only | Nx | 0.5° x 0.625° | 1 level | Surface data fields (e.g. PS, EVAP, HFLUX, etc.) |
|
| Model level | Nv | 0.5° x 0.625° | 72 hybrid levels | Most 3D data fields (e.g. U, V, T, etc.) |
Vertical levels are identical to GEOS-5, MERRA, and GEOS-FP data |
| Model edges | Ne | 0.5° x 0.625° | 73 hybrid level edges | Data fields defined on level edges (e.g. CMFMC, PLE, etc.) |
Vertical level edges are identical to GEOS-5.2.0, MERRA, and GEOS-FP data |
| Pressure | Np | 0.5° x 0.625° | 42 pressure levels: 1000, 975, 950, 925, 900, 875, |
Various 3D data fields | We do not use of the pressure-level for GEOS-Chem. We only use data on the Nx, Nv, Ne grids. |
Output grids
We download the MERRA-2 data at its native 0.5° x 0.625° horizontal resolution. For use with GEOS-Chem, we cut and/or regrid the 0.5° x 0.625° data to the following grids:
- GEOS-Chem 0.5° x 0.625° nested grids for Asia (China + India), Europe, and North America.
- GEOS-Chem 2° x 2.5° grid
- GEOS-Chem 4° x 5° grid
--Bob Yantosca (talk) 22:49, 28 November 2016 (UTC)
MERRA-2 file naming convention
The following description of the naming convention used for MERRA "raw" data files is paraphrased and adapted from Section 5.1 and 5.2 of the MERRA File Specification Document, pp 10ff:
Standard names
The standard full name for the assimilated GEOS-5 MERRA-2 products will consist of five dot-delimited nodes:
runid.collection.timestamp.nc4
The node fields, which vary from file to file, are defined as follows:
- runid
- For mainstream MERRA data, the following runid's are used:
- MERRA400: Years from ?? -??
- collection
- Collection names are of the form freq_dims_group_HV, where the four attributes are:
- freq: time-independent (cnst), instantaneous (instF), or time-average (tavgF), where F indicates the frequency or averaging interval and can be any of the following:
- 1 = Hourly
- 3 = 3-Hourly
- 0 = Not Applicable
- dims: Can be either:
- 2d for collections with only 2-dimensional fields or
- 3d for collections with a mix of 2- and 3-dimensional fields.
- group: A three-letter mnemonic for the type of fields in the collection.
- HV: Horizontal and Vertical grid.
- H can be:
- N: Native (0.5° x 0.625°) horizontal resolution
- V can be:
- x: horizontal-only data (surface, single level, etc.) ; dims must be 2D
- p: pressure-level data (see Appendix D for levels) ; dims must be 3D
- v: model layer centers (see Appendix D ) dims must be 3D
- e: model layer edges (see Appendix D ) dims must be 3D
- timestamp
- This node defines the date and time associated with the data in the file. It has the form yyyymmdd
- yyyy - year string (e.g. , 2002)
- mm - month string (e.g.., 09 for September)
- dd - day of the month string
- nc4
- Denotes that the data is being saved in a netCDF-4 file.
EXAMPLE:
MERRA-2_400.tavg1_2d_flx_Nx.20150101.nc4
This is an example of a MERRA-2 filename from the production segment of the original version of the fourth (most recent) assimilation stream. The data are time-averaged, two-dimensional, surface flux products, at native horizontal resolution. The file contains all data for 01 Jan 2015.
--Bob Y. (talk) 20:19, 31 July 2015 (UTC)
ESDT names
As required by the EOSDIS system, all GEOS-5 FP products are identified by a relatively short ESDT name. While GEOS-5 FP products are not currently distributed from the GES DISC, we have retained the ESDT designations for assimilation products. This name, also known as the ShortName, is a short handle for users to access and order data products. It takes the form: DFPTFHVGGG, where: where
- T: Time Description:
- I = Instantaneous
- T = Time-averaged
- C = Time-independent
- F: Frequency
- 0 = Time-independent
- 1 = Hourly
- 3 = 3-Hourly
- H: Horizontal Resolution
- N = Native
- V: Vertical Location
- X = Two-dimensional
- P = Pressure
- V = model layer center
- E = model layer edge
- GGG: Group
- ASM = assimilated state variables (from the IAU corrector, see Appendix A)
- TDT = tendencies of temperature
- UDT = tendencies of eastward and northward wind components
- QDT = tendencies of specific humidity
- ODT = tendencies of ozone
- LND = land surface variables
- FLX = surface turbulent fluxes and related quantities
- MST = moist processes
- CLD = cloud-related quantities
- RAD = radiation
- TRB = turbulence
- SLV = single level
- INT = vertical integrals
- CHM = chemistry forcing
- AER = aerosol diagnostics
- ADG = aerosol diagnostics (extended)
- LSF = large-scale flux
- OCN = ocean
- LFO = land-surface forcing
- NAV = navigation
--Bob Y. 15:50, 16 August 2013 (EDT)
MERRA-2 data file collections
NOTE: the ESDT name may not be correct. We are waiting for the MERRA-2 file spec to be released, and will correct the entries in the table below at that time.
This table shows only those MERRA-2 file collections that are required for GEOS-Chem.
NOTES:
- All data is on the native horizontal grid (0.6125° lon x 0.5deg; lat, 576 x 361 grid boxes)
- Horizontal arrays have dimensions 576 (lon) x 361 (lat) x 72 (levels)
- Longitudes increase eastward, starting at -180°
- Latitudes increase northward, starting at -90°
- For files containing 3D data:
- Level 1 corresponds to the top of the atmosphere
- Level 72 corresponts to the surface
| File Collection Name |
ESDT Name (aka "Shortname") |
Description | Times | Approx daily size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| const_2d_asm_Nx | D??C0NXASM | Constant fields | Time-invariant | 5 |
| inst3_3d_asm_Nv | D??I3NVASM | Basic assimilated fields from IAU corrector | Instantaneous values every 3 hours | 2,250 |
| tavg3_3d_asm_Nv | D??T3NVASM | Upper-air wind tendencies by process | 3-hour time-averaged values | 2,240 |
| tavg3_3d_cld_Nv | D??T3NVCLD | Upper-air cloud related diagnostics | 3-hour time-averaged values | 730 |
| tavg3_3d_mst_Nv | D??T3NVMST | Upper-air diagnostics from moist processes at layers | 3-hour time-averaged values | 840 |
| tavg3_3d_mst_Ne | D??T3NEMST | Upper-air diagnostics from moist processes at layers | 3-hour time-averaged values | 268 |
| tavg1_2d_flx_Nx | D??T1NXFLX | Surface fluxes and related quantities | 1-hour time-averaged values | 400 |
| tavg1_2d_lnd_Nx | D??T1NXLND | Land related surface quantities | 1-hour time-averaged values | 206 |
| tavg1_2d_rad_Nx | D??T1NXRAD | Surface and TOA radiative fluxes | 1-hour time-averaged values | 218 |
| tavg1_2d_slv_Nx | D??T1NXSLV | Single-level atmospheric state variables | 1-hour time-averaged values | 420 |
| TOTAL | 7,577 |
As described above, the full file name for the GEOS-FP data products takes the form:
MERRA-2_SSS.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC.YYYYMMDD.nc4
where
- SSS is the MERRA-2 stream name (currently "400")
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC is the collection name (i.e. one of the entries in the first column of the above table)
- YYYYMMDD is the UTC date (year/month/day)
--Bob Y. (talk) 20:25, 31 July 2015 (UTC)
MERRA-2 time archiving
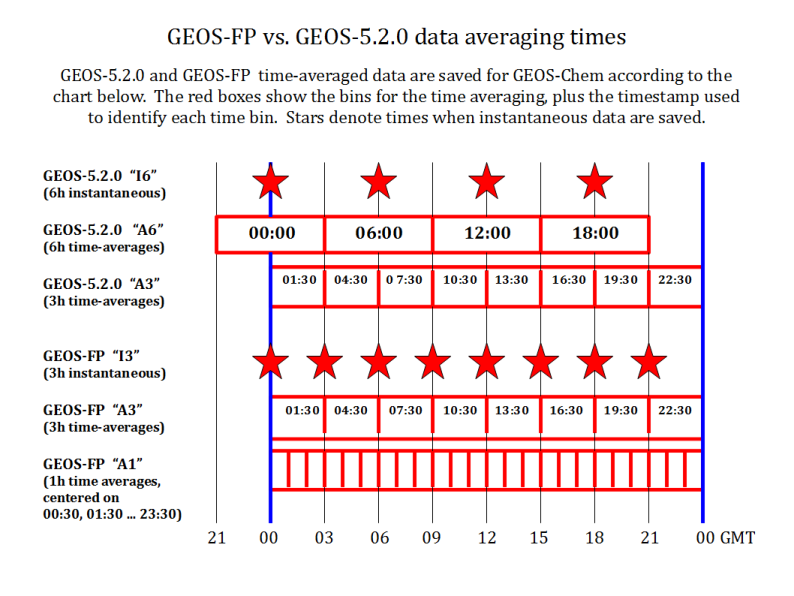
NOTE: MERRA-2 uses the identical time archiving as the GEOS-5 "forward processing" data product (i.e. what we refer to as GEOS-FP).
Raw data
The MERRA-2 raw data are archived/averaged at the following times:
| Collections | Description | Timestamps |
|---|---|---|
| const_2d_asm_Nx | Time-invariant data | N/A |
| inst3_3d_asm_Nv | Instantaneous (snapshot) data, every 3 hours | 00:00, 03:00, 06:00, 09:00, 12:00, 15:00, 18:00, 21:00 UTC |
| tavg1_2d_flx_Nx tavg1_2d_lnd_Nx tavg1_2d_rad_Nx tavg1_2d_slv_Nx |
1-hour time-averaged data | 00:30, 01:30, 02:30 ... 23:30 UTC
|
| tavg3_3d_asm_Nv tavg3_3d_cld_Nv tavg3_3d_mst_Ne tavg3_3d_mst_Nv |
3-hour time-averaged data | 01:30, 04:30, 07:30, 10:30, 13:30, 16:30, 19:30, 22:30 UTC
|
--Bob Y. (talk) 20:54, 31 July 2015 (UTC)
Processed data
The processed MERRA-2 data for GEOS-Chem shall keep the same temporal resolution as the MERRA-2 raw data. To prevent file sizes from becoming larger than 2GB (i.e. the maximum netCDF-3 file size), we split the regridded MERRA-2 data among the following file types:
| Filenames | Description | Timestamps |
|---|---|---|
| MERRA-2.20150101.CN.{RES}.nc | Time-invariant data | For convenience we assign a file timestamp of 2015/01/01 at 00:00 GMT. |
| MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.A1.{RES}.nc | 1-hour time-averaged data | 00:30, 01:30, 02:30 ... 23:30 UTC
|
| MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.A3cld.{RES}.nc MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.A3dyn.{RES}.nc MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.A3mstC.{RES}.nc MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.A3mstE.{RES}.nc |
3-hour time-averaged data | 01:30, 04:30, 07:30, 10:30, 13:30, 16:30, 19:30, 22:30 UTC
|
| MERRA-2.YYYYMMDD.I3.{RES}.nc | 3-hour time-averaged data | 00:00, 03:00, 06:00, 09:00, 12:00, 15:00, 18:00, 21:00 UTC |
In the filenames abaove, the {RES} tag indicates the horizontal resolution of the file. Possible values are:
| {RES} | Description |
|---|---|
| 4x5 | GEOS-Chem 4° x 5° global grid |
| 2x25 | GEOS-Chem 2° x 2.5° global grid |
| 05x0625.CH | GEOS-Chem 0.5° x 0.625° China nested grid |
| 05x0625.EU | GEOS-Chem 0.5° x 0.625° Europe nested grid |
| 05x0625.CH | GEOS-Chem 0.5° x 0.625° North America nested grid |
| 05x0625.CH | GEOS-Chem 0.5° x 0.625° SE Asia nested grid |
The A1 and A3 files use the following bins for time-averaging. The file timestamps in the data files indicate the center of the time-averaging bins.
NOTE: MERRA-2 uses the same timing scheme as the data marked in the plot as "GEOS-FP". (We will eventually update the image below.)
Please also see our List of MERRA-2 met fields wiki page for detailed information about which fields are stored in each of these file types.
--Bob Y. (talk) 21:09, 31 July 2015 (UTC)
Implementation into GEOS-Chem
Please see our MERRA-2 implementation details wiki page for more information about how we modified GEOS-Chem for use with the GEOS-FP met field product.
--Bob Y. (talk) 21:11, 31 July 2015 (UTC)
References
- GEOS5-FP file specification document, Version 1.0 (11 Jun 2013)
- Bacmeister, J. T., M. J. Suarez, and F. R. Robertson, 2006. Rain Re-evaporation, Boundary Layer Convection Interactions, and Pacific Rainfall Patterns in an AGCM. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 3383-3403.
- Bloom, S., L. Takacs, A. DaSilva, and D. Ledvina, 1996: Data assimilation using incremental analysis updates. Mon. Wea. Rev., 124, 1256-1271.
- Derber, J. C., R. J. Purser, W.-S. Wu, R. Treadon, M. Pondeca, D. Parrish, and D. Kleist, 2003: Flow-dependent Jb in a global grid-point 3D-Var. Proc. ECMWF annual seminar on recent developments in data assimilation for atmosphere and ocean. Reading, UK, 8-12 Sept. 2003.
- Koster, R. D., M. J. Suárez, A. Ducharne, M. Stieglitz, and P. Kumar, 2000: A catchment-based approach to modeling land surface processes in a GCM, Part 1, Model Structure. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 24809-24822.
- Molod, A., L. Takacs, M. Suarez, J. Bacmeister, I. Song, and A. Eichmann, The GEOS-5 Atmospheric General Circulation Model: Mean Climate and Development from MERRA to Fortuna, Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation, 28, Ed: Max J. Suarez, NASA GMAO, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD, April 2012. (PDF)
- Rienecker, M.M., M.J. Suarez, R. Todling, J. Bacmeister, L. Takacs, H.-C. Liu, W. Gu, M. Sienkiewicz, R.D. Koster, R. Gelaro, I. Stajner, and E. Nielsen, 2008: The GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System - Documentation of Versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0. Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation 104606, v27.
- Wu, W.-S., R.J. Purser and D.F. Parrish, 2002: Three-dimensional variational analysis with spatially inhomogeneous covariances. Mon. Wea. Rev., 130, 2905-2916.