Merging
Overview
On this page, we provide information about merging branches together, as well as rebasing branches (i.e. putting all the commits in a branch on top of another branch).
Merging
Merging is the process of combining two Git branches together. It can be done either from the Git GUI (our recommended method), or from the command line.
Merging with the Git GUI
Follow these steps to merge branches together with the Git gui.
1. Open the Git GUI
git gui &
2. Checkout the target branch—the branch you wish to merge another branch into. In this cas
When you are ready to merge your changes back into the mainline master branch, then you can follow this procedure.
- Switch back to the master branch by selecting Branch/Checkout from the menu (or type CTRL-O). You will be given a dialog box of available branches. Select master and click Checkout.
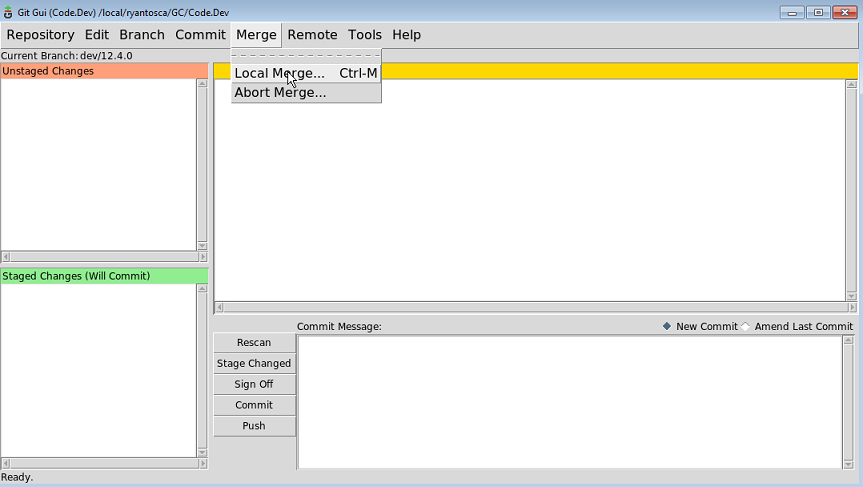
- From the menu, pick Merge/Local Merge (or CTRL-M).
You will be given a dialog box of available branches. Select the branch you would like to merge into master and click Merge.
This should merge your changes back into master. If you then start the gitk viewer, you should see your changes merged into the master branch.
Merging from the command line
Resolving conflicts caused by a merge
Sometimes you may encounter conflicts when merging one branch into another branch. This can happen when you are merging code from an older GEOS-Chem version into the latest version. A conflict is just Git saying, "I found some code in a place where I didn't expect to find it. Can you help me figure out which lines of code to keep and which to throw away?"
When you encounter a conflict, open the git gui window. You will see each file containing a conflict listed in the Unstaged Changes window. Clicking on each file will display the lines of code where the conflicts are located. You will see one or more slugs in the file. A slug is a block of text that displays the source code from the old branch and the new branch.
<<<<<<< HEAD ! This is old source code that already exists in the branch ... ======= ! This is new source code that is being merged into the branch ... >>>>>>> 77976da35a11db4580b80ae27e8d65caf5208086
At the top of the slug you see the string <<<<<<< HEAD followed by some source code. This is the "old" code, i.e. the code that existed as of the last commit. A separator line ======= then follows the source code.
Underneath the separator line, you will see the "new" source code, i.e. the code that we are merging into the branch. This source code is followed by the text >>>>>>> 77976da35a11db4580b80ae27e8d65caf5208086. The long numeric string is the SHA1 ID (the internal ID # used by Git) corresponding to the commit that we are merging into the branch. Each commit has a unique SHA1 ID.
To resolve a file containing conflicts, do the following:
- Open the file in your favorite text editor (vi, emacs, etc.)
- Search for the word HEAD. This will take you to the location of each slug (where conflicts exist).
- Decide which code that you want to keep.
- Delete the code that you do not want to keep.
- Delete the lines <<<<<<< HEAD, =======, and >>>>>>> 7797... If you keep these in the source code you will get compilation errors.
- Repeat this process for each conflict that you find.
Once you have resolved the conflicts in each file, you can commit them back into the repository.