GEOS-Chem 1-month benchmark timing results: Difference between revisions
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Timing information is obtained from the GEOS-Chem "Timers" output, which is printed to the log file. Timers output is activated when compiling GEOS-Chem with <tt>TIMERS=y</tt> (GNU Make) or <tt>-DTIMERS=y</tt> and turning on timers in input.geos. | Timing information is obtained from the GEOS-Chem "Timers" output, which is printed to the log file. Timers output is activated when compiling GEOS-Chem with <tt>TIMERS=y</tt> (GNU Make) or <tt>-DTIMERS=y</tt> and turning on timers in input.geos. | ||
== For more information == | == For more information == | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 29 June 2021
Previous | Next | Guide to GEOS-Chem performance
- Parallelizing GEOS-Chem
- GEOS-Chem 7-day timing tests
- GEOS-Chem scalability
- GEOS-Chem 1-month benchmark timing results
- Profiling GEOS-Chem with the TAU performance system
- Speeding up GEOS-Chem
Overview
On this page, we provide timing results obtained from 1-month benchmark GEOS-Chem simualtions.
Timing results from 1-month benchmarks
To access the entire history of GEOS-Chem benchmarks, please see our GEOS-Chem versions page.
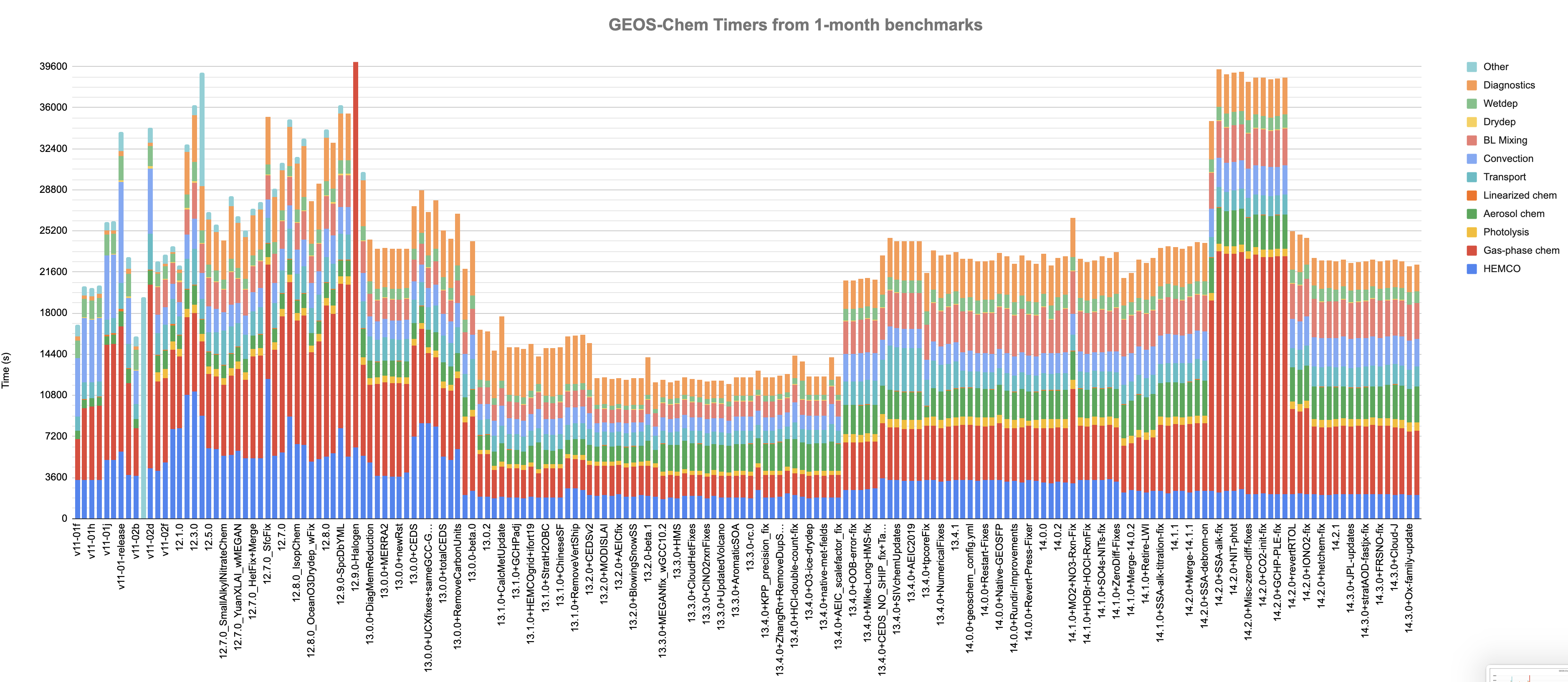
Wall time spent in model components
The above plot displays the "wall clock" time spent in each model component as observed in the GEOS-Chem timers output from recent public and internal 1-month benchmark simulations (Credit: Melissa Sulprizio). This type of plot can be very helpful in determining if updates made to GEOS-Chem cause significant computational bottlenecks.
Timing information is obtained from the GEOS-Chem "Timers" output, which is printed to the log file. Timers output is activated when compiling GEOS-Chem with TIMERS=y (GNU Make) or -DTIMERS=y and turning on timers in input.geos.
For more information