Tagging: Difference between revisions
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
git tag -d TAG_NAME | git tag -d TAG_NAME | ||
== Further reading === | |||
TBD | |||
---- | ---- | ||
'''''[[Committing|Previous]] | [[Merging|Next]] | [[Guide to using Git with GEOS-Chem]] | [[Getting Started with GEOS-Chem]] | [[Main Page|GEOS-Chem Main Page]]''''' | '''''[[Committing|Previous]] | [[Merging|Next]] | [[Guide to using Git with GEOS-Chem]] | [[Getting Started with GEOS-Chem]] | [[Main Page|GEOS-Chem Main Page]]''''' | ||
Revision as of 17:25, 20 June 2019
Previous | Next | Guide to using Git with GEOS-Chem | Getting Started with GEOS-Chem | GEOS-Chem Main Page
Overview
On this page, we describe how to add tags to individual commits.
Tagging
Git allows you to tag a particular commit with an alphanumeric string for easy reference. This tag can be used with git pull', git checkout, etc. commands in the same way as for branches.
Each commit corresponding to a GEOS-Chem version release is tagged with the version number (e.g. 12.3.2).
Create at tag using Gitk
You may also add a tag via the gitk viewer utility, as follows:
1. Start Gitk:
gitk --all
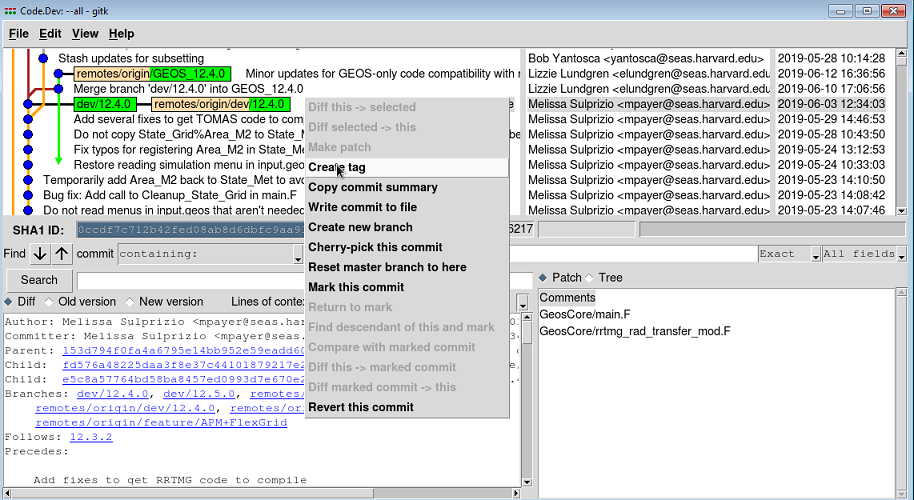
2. Select the commit that you wish to tag by right-clicking on its name with your mouse. A context menu will appear:
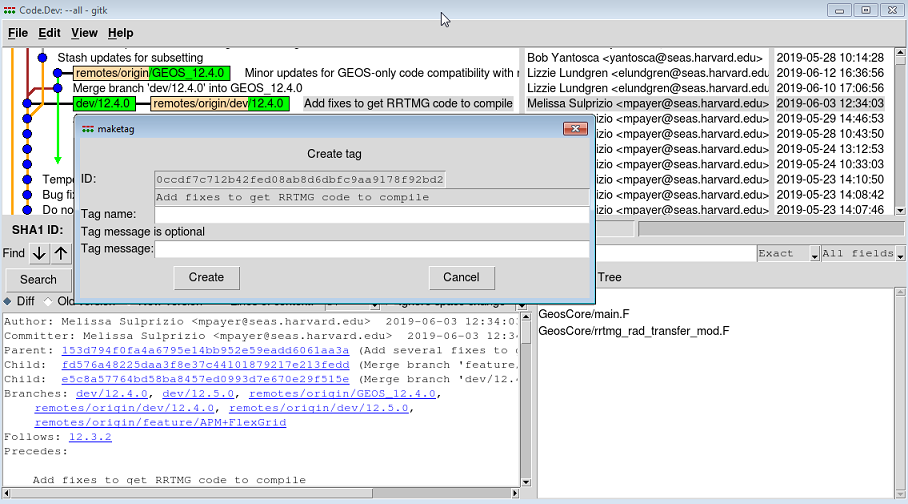
3. Select the 'Create tag option. This will pop open a dialog box:
4. Type the name of the tag in the Tag name box.
5. Click on Create.
Create a tag from the command line
You can add a tag via the command line:
git tag GEOS-Chem TAG_NAME
That command will create a tag at the current commit.
Removing tags
You can remove a tag via the command line:
git tag -d TAG_NAME
Further reading =
TBD
Previous | Next | Guide to using Git with GEOS-Chem | Getting Started with GEOS-Chem | GEOS-Chem Main Page